Linux驱动开发——字符设备驱动
字符设备驱动是Linux内核中用于管理字符设备(如终端、串口等)的模块,它以字节流的形式进行数据读写。以下是字符设备驱动的编写流程及主要函数说明:
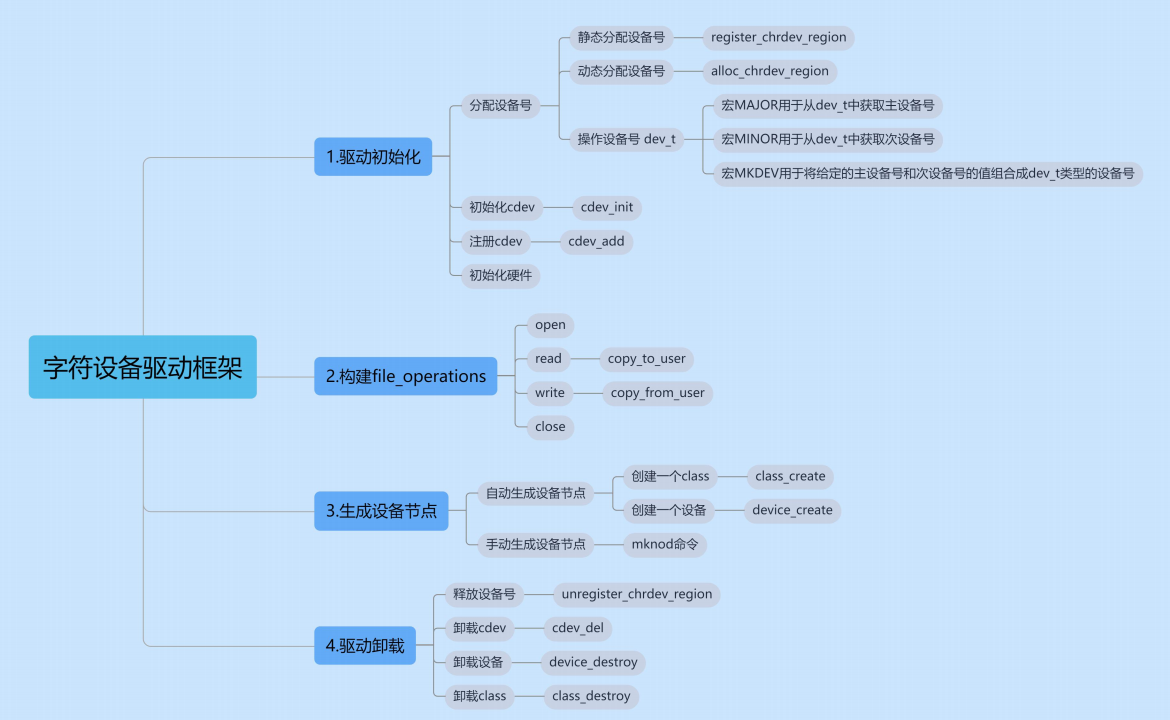
编写流程
分配设备号
- 静态分配:
register_chrdev_region() - 动态分配:
alloc_chrdev_region()
- 静态分配:
创建设备结构体
- 定义并初始化
struct cdev结构体
- 定义并初始化
初始化cdev结构体
- 使用
cdev_init()函数
- 使用
添加cdev到系统
- 使用
cdev_add()函数
- 使用
创建设备文件节点
- 手动创建:
mknod命令 - 自动创建:使用
class_create()和device_create()
- 手动创建:
实现文件操作集合
- 定义并填充
struct file_operations结构体
- 定义并填充
编写具体的操作函数
- 如
open,read,write,ioctl,release等
- 如
注销设备
- 使用
cdev_del()和unregister_chrdev_region()
- 使用
主要函数及参数定义
1. 设备号注册/注销
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name);
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name);
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count);
from:设备号(主设备号+次设备号)count:连续设备号的数量name:设备名称(出现在/proc/devices)dev:用于返回分配的第一个设备号baseminor:请求的第一个次设备号
2. cdev操作
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops);
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count);
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p);
cdev:要初始化的cdev结构体指针fops:文件操作集合p:要添加/删除的cdev结构体指针dev:设备号count:设备数量
3. 自动创建设备节点
struct class *class_create(struct module *owner, const char *name);
struct device *device_create(struct class *cls, struct device *parent,
dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...);
void device_destroy(struct class *cls, dev_t devt);
void class_destroy(struct class *cls);
owner:通常为THIS_MODULEname:类名称cls:所属类parent:父设备(通常为NULL)devt:设备号drvdata:驱动私有数据fmt:设备名称格式字符串
4. 文件操作结构体(struct file_operations)
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
// 其他成员...
};
5. 主要操作函数参数说明
open/release
int (*open)(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp);
int (*release)(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp);
inode:包含设备号等信息filp:文件结构,可存储私有数据
read/write
ssize_t (*read)(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos);
ssize_t (*write)(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos);
buf:用户空间缓冲区count:请求传输的字节数f_pos:文件位置指针
ioctl
long (*unlocked_ioctl)(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
cmd:用户请求的命令arg:命令参数
示例代码框架
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#define DEVICE_NAME "mydev"
static int major;
static struct cdev my_cdev;
static struct class *my_class;
static int my_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { ... }
static int my_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { ... }
static ssize_t my_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos) { ... }
static ssize_t my_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos) { ... }
static struct file_operations fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = my_open,
.release = my_release,
.read = my_read,
.write = my_write,
};
static int __init my_init(void)
{
dev_t dev;
// 分配设备号
alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 1, DEVICE_NAME);
major = MAJOR(dev);
// 初始化cdev
cdev_init(&my_cdev, &fops);
my_cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
// 添加cdev到系统
cdev_add(&my_cdev, dev, 1);
// 创建设备类
my_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "my_class");
// 创建设备节点
device_create(my_class, NULL, dev, NULL, DEVICE_NAME);
return 0;
}
static void __exit my_exit(void)
{
dev_t dev = MKDEV(major, 0);
device_destroy(my_class, dev);
class_destroy(my_class);
cdev_del(&my_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(dev, 1);
}
module_init(my_init);
module_exit(my_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
以上是字符设备驱动的基本编写流程和主要函数说明,实际开发中还需要考虑并发控制、阻塞/非阻塞I/O、内存管理等问题。
点灯完整代码
以泰山派RK3566为例
led_drv.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/io.h>
#define MY_NAME "hx_led"
#define PMU_GRF_GPIO3B_IOMUX_H 0xFDC6004C
#define GPIO_SWPORT_DDR_L 0xFE760008
#define GPIO_SWPORT_DR_L 0xFE760000
int major = 0;
char kbuf[128] = {0};
unsigned int *virt_iomux;
unsigned int *virt_ddr;
unsigned int *virt_dr;
static struct class *led_class;
int my_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("open!\n");
return 0;
}
ssize_t my_read (struct file *file, char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf);
if(copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size))
{
printk("copy data to user fail!\n");
return -EIO;
}
return size;
}
ssize_t my_write (struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *offset)
{
if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf);
if(copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size))
{
printk("copy data form user fail!\n");
return -EIO;
}
if(kbuf[0] == '1')
{
//0xFE760000 12位写1(设置输出高电平) 28位写1(写使能)
*virt_dr |= 0x10001000;
}
return size;
}
int my_close (struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("close!\n");
return 0;
}
struct file_operations fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = my_open,
.read = my_read,
.write = my_write,
.release = my_close
};
int my_led_init(void)
{
virt_iomux = ioremap(PMU_GRF_GPIO3B_IOMUX_H, 4);
if(virt_iomux == NULL)
{
printk("ioremap iomux register error! \n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
virt_ddr = ioremap(GPIO_SWPORT_DDR_L, 4);
if(virt_ddr == NULL)
{
printk("ioremap ddr register error! \n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
virt_dr = ioremap(GPIO_SWPORT_DR_L, 4);
if(virt_dr == NULL)
{
printk("ioremap dr register error! \n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
//0xFDC6004C 0-2位写0(gpio功能) 16-18 写1(写使能)
*virt_iomux |= 0x70000;
//0xFE760008 12位写1(设置为输出) 28位写1(写使能)
*virt_ddr |= 0x10001000;
//0xFE760000 12位写0(设置输出低电平) 28位写1(写使能)
*virt_dr |= 0x10000000;
return 0;
}
static int __init mycdev_init(void)
{
int err;
major = register_chrdev(0, MY_NAME, &fops);
if(major < 0)
{
printk("reg failed!\n");
return -1;
}
//
led_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hx_led_class");
err = PTR_ERR(led_class);
if (IS_ERR(led_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "led");
return -1;
}
device_create(led_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hx_led0");
//
printk("reg successed\n");
my_led_init();
return 0;
}
int my_led_deinit(void)
{
//0xFE760000 12位写0(设置输出低电平) 28位写1(写使能)
*virt_dr |= 0x10000000;
iounmap(virt_iomux);
iounmap(virt_ddr);
iounmap(virt_dr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit mycdev_exit(void)
{
my_led_deinit();
printk("hello world %s\n","exit");
device_destroy(led_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(led_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, MY_NAME);
}
module_init(mycdev_init);
module_exit(mycdev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("hx");
app.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
int fd = open("/dev/hx_led",O_RDWR);
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("open failed");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
write(fd,"1",1);
usleep(200000);
write(fd,"0",1);
usleep(200000);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
Makefile
KERN_DIR = /home/hxbj/tspi/linux/kernel
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o app app.c
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
rm -f app
obj-m += led_drv.o
本文是原创文章,采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议,完整转载请注明来自 恒星不见
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果


